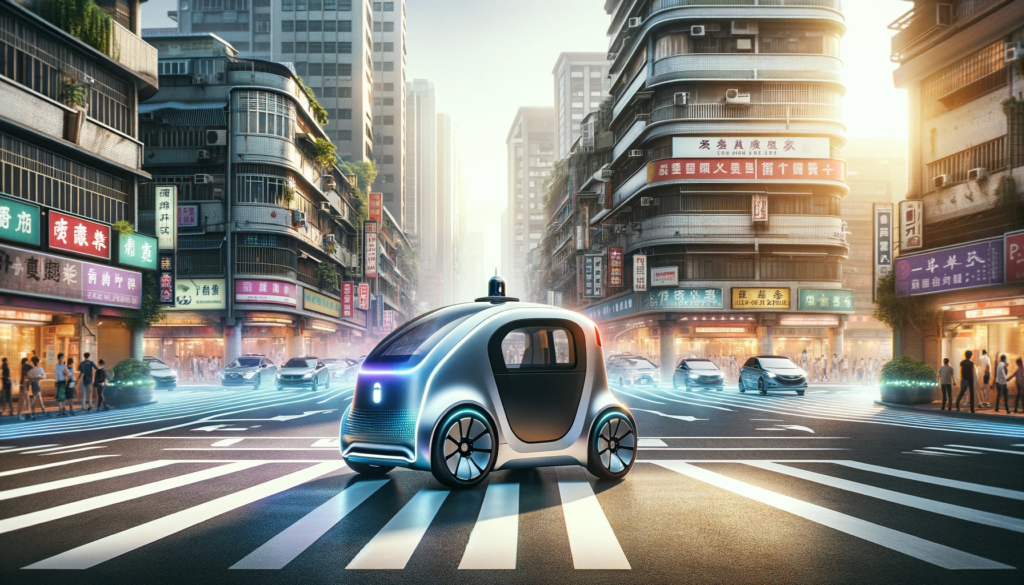
The Future of Transportation: Taiwan Self-Driving Gharry
The future of transportation is rapidly changing, with new technologies paving the way for a more efficient, safer, and environmentally-friendly world. Among the most exciting developments is the concept of the self-driving vehicle. One innovation that has captured attention in recent years is the Taiwan Self-Driving Gharry. A unique blend of tradition and technology, this self-driving carriage has the potential to revolutionize both the transportation industry and Taiwan’s tourism sector. In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of the Taiwan self-driving gharry, exploring its design, technological advancements, societal impacts, and the future it holds.
What is a Taiwan Self-Driving Gharry?
A Taiwan Self-Driving Gharry is a modern reinvention of the traditional horse-drawn carriage, or gharry, which has been used for centuries as a means of transportation in various parts of the world. The self-driving version, however, removes the need for human drivers or animals to operate it, relying entirely on automation and artificial intelligence (AI) to navigate its route. The vehicle is equipped with sensors, cameras, GPS, and complex algorithms that allow it to move autonomously through various terrains, offering a smooth and efficient ride to its passengers.
While the original gharry is still in use in some parts of Taiwan for cultural and tourist activities, the self-driving version represents a significant technological leap. It blends the nostalgic charm of a traditional mode of transport with the cutting-edge advancements of the 21st century.
How Does the Taiwan Self-Driving Gharry Work?
The technology behind the Taiwan self-driving gharry involves a combination of several cutting-edge innovations in robotics, artificial intelligence, and vehicle automation. Here’s a closer look at the components that enable these carriages to operate autonomously:
1. Autonomous Navigation Systems
At the heart of any self-driving vehicle is its autonomous navigation system. The Taiwan self-driving gharry uses a highly sophisticated navigation system, which includes GPS, lidar (light detection and ranging), and ultrasonic sensors. These systems work in tandem to map out the surrounding environment and create a digital representation of the vehicle’s surroundings. This allows the gharry to detect obstacles, avoid collisions, and find the best route to its destination.
2. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
The artificial intelligence embedded within the Taiwan self-driving gharry allows it to make real-time decisions based on the data it collects from its sensors. For instance, the AI system helps the gharry recognize traffic signs, pedestrians, and other vehicles, ensuring safe operation. Machine learning algorithms also allow the vehicle to improve its decision-making abilities over time, making the ride smoother and more efficient with each trip.
3. Safety Features
Safety is a critical aspect of any self-driving vehicle, and the Taiwan self-driving gharry is no exception. It comes equipped with an array of safety features, such as emergency braking, collision detection, and adaptive cruise control. These features ensure that the gharry can handle unexpected obstacles or changes in the environment, making it a reliable and safe mode of transportation.
Applications of the Taiwan Self-Driving Gharry
1. Tourism and Leisure
One of the most exciting applications of the Taiwan self-driving gharry is in the tourism industry. Traditional horse-drawn carriages have long been a staple of Taiwan’s tourist experiences, especially in scenic areas such as Taroko Gorge and the historical sites in Tainan. The self-driving gharry presents an opportunity to modernize this experience without losing the charm of the past.
With autonomous capabilities, tourists can enjoy guided tours with enhanced comfort and safety, without the concern of needing a human driver. These vehicles could operate on set routes, offering visitors an immersive, automated experience of Taiwan’s most beautiful and culturally significant locations.
2. Urban Mobility
The Taiwan self-driving gharry could also contribute to the future of urban mobility, particularly in areas where traffic congestion and pollution are pressing concerns. Self-driving gharrys can potentially serve as an eco-friendly, cost-effective alternative to traditional taxis or buses, offering residents and tourists an easy way to travel short distances within city centers.
By replacing traditional vehicles with self-driving carriages, Taiwan could make a significant dent in reducing carbon emissions and improving urban mobility. Additionally, self-driving gharrys could be deployed in high-demand areas, helping reduce traffic congestion and the need for parking spaces.
3. Accessibility
The Taiwan self-driving gharry is also poised to offer improved accessibility for individuals with mobility challenges. With automated systems in place, these vehicles can be designed to cater to those who may not be able to operate traditional vehicles. This could include elderly passengers or those with physical disabilities, making transportation more inclusive for all.
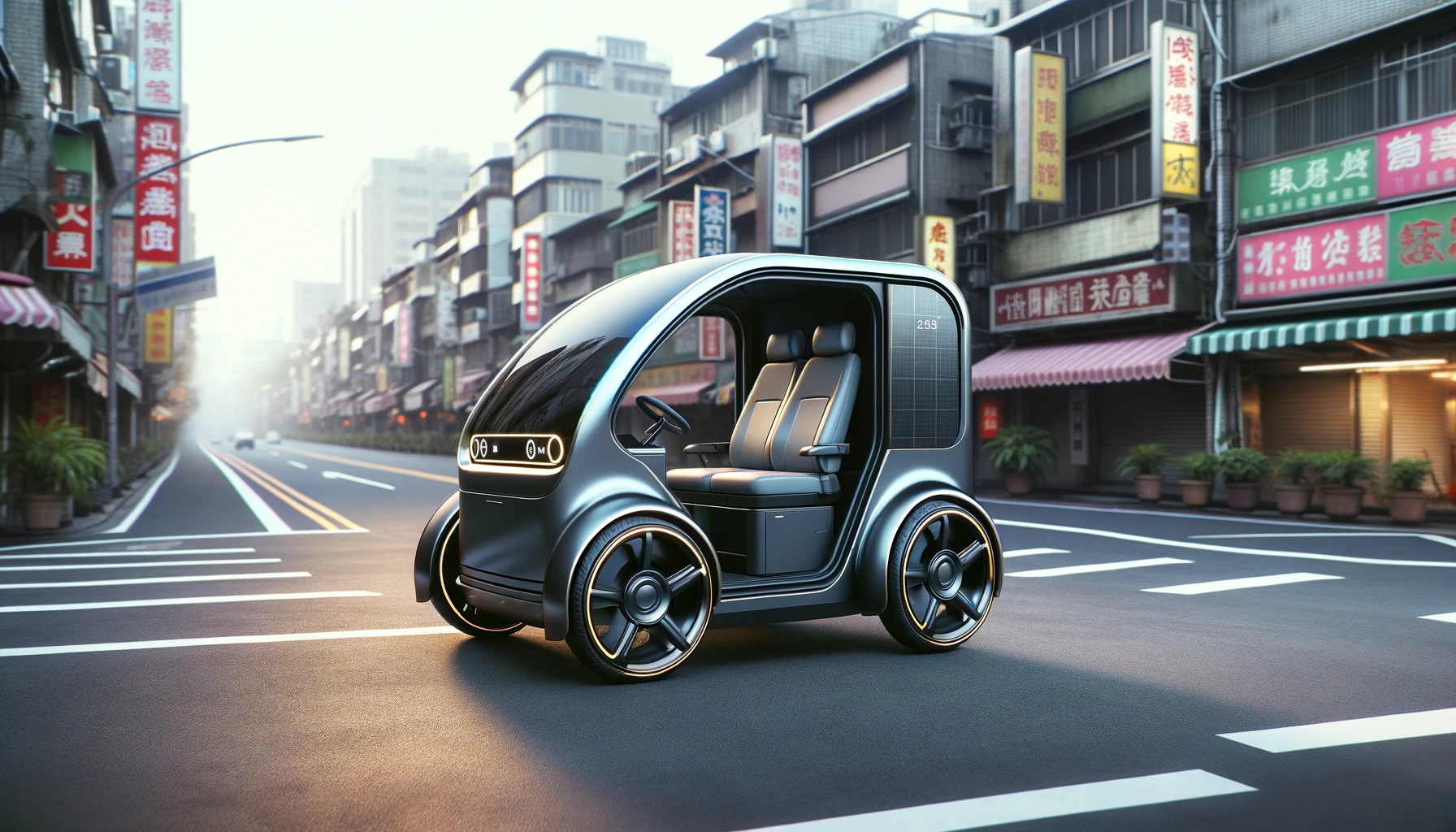

The Role of Taiwan’s Government and Technological Infrastructure
For the Taiwan self-driving gharry to become a mainstream mode of transportation, it requires significant support from both the government and the private sector. Taiwan has long been a hub for technological innovation, and the government has been proactive in supporting research and development in the autonomous vehicle space. However, to ensure the widespread deployment of the self-driving gharry, several key factors must be addressed:
1. Regulatory Framework
A comprehensive regulatory framework is needed to govern the use of autonomous vehicles in Taiwan. This includes setting standards for safety, performance, and insurance. Regulations must also ensure that the vehicles are compatible with existing infrastructure, such as roads, traffic signals, and pedestrian pathways.
2. Infrastructure Development
Alongside regulation, Taiwan will need to invest in infrastructure that supports self-driving technology. This includes updating roads with sensors and smart traffic management systems that can communicate with autonomous vehicles, as well as establishing charging stations for electric-powered self-driving gharrys.
Potential Challenges and Considerations
Despite the promising future of the Taiwan self-driving gharry, there are several challenges to overcome before these vehicles can be fully integrated into everyday life.
1. Public Acceptance
Public acceptance of autonomous vehicles is one of the most significant hurdles. Many people are still hesitant about riding in self-driving vehicles due to concerns over safety and reliability. To gain the trust of the public, there must be a continuous effort to educate people on the benefits of autonomous technology and address any concerns regarding its safety.
2. Technical and Operational Hurdles
Although the technology behind self-driving vehicles has come a long way, there are still several technical challenges to overcome. These include ensuring the vehicle can operate efficiently in all weather conditions, handling complex traffic scenarios, and maintaining system reliability over time.

Conclusion: The Bright Future of the Taiwan Self-Driving Gharry
The Taiwan self-driving gharry is an exciting innovation that blends traditional transportation with modern technology. With its ability to enhance tourism, promote urban mobility, and increase accessibility, it has the potential to play a significant role in the future of transportation. However, for this vision to become a reality, Taiwan must continue to support research, invest in infrastructure, and address the challenges related to public acceptance and technical capabilities.
As the world moves towards a more automated future, the Taiwan self-driving gharry represents not just a mode of transport, but a glimpse into a future where technology and tradition coexist seamlessly. With continued advancements, this self-driving carriage could become a symbol of Taiwan’s commitment to sustainable and innovative transportation solutions.